If you are someone who needs to perform research and make sense of large datasets, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of various AI tools can significantly enhance your productivity and accuracy. Recently, we tested three leading AI's—Alani AI, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, and Google Notebook LM—to evaluate their proficiency in analyzing the Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) initiatives of three major tech companies: NVIDIA, Microsoft, and Google. This article presents both qualitative and quantitative findings of this comparative analysis, demonstrating why Alani AI emerged as the clear leader.
The Test
Each AI model was given the same dataset and asked the same set of questions regarding the ESG initiatives of NVIDIA, Microsoft, and Google. Click here to see the files used in this test. The responses were evaluated based on five key criteria:
- Depth of Analysis
- Specificity of Examples
- Comparative Insight
- Identification of Conflicts
- Overall Clarity and Structure
To make it objective, we had ChatGPT score each criterion out of 10, and the total score for each AI was calculated. Here's a detailed breakdown of the results:
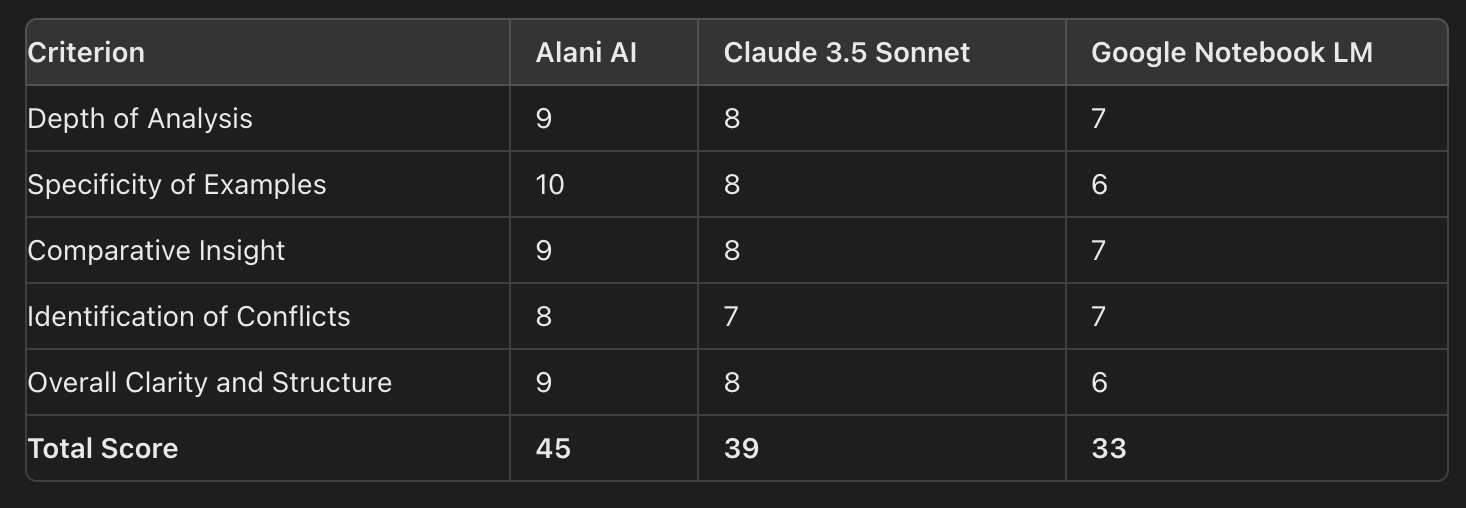
Quantitative Analysis
To provide a clearer perspective, we calculated how much better Alani AI performed compared to the other AI models:
- Alani AI vs. Claude 3.5 Sonnet: Alani AI performed approximately 15.4% better.
- Alani AI vs. Google Notebook LM: Alani AI performed approximately 36.4% better.
How We Arrived at These NumbersTo ensure an objective and thorough evaluation, we used a detailed rubric for each criterion:
Depth of Analysis: We assessed how thoroughly each AI model analyzed the ESG efforts of the three companies. This included the breadth and depth of the topics covered. Points were awarded based on the comprehensiveness of the analysis:
- 10 points: Exhaustive analysis covering all major ESG dimensions (environmental, social, governance).
- 8-9 points: Detailed analysis with minor gaps.
- 6-7 points: General analysis with significant gaps.
- 5 points or below: Superficial analysis with many missing elements.
Specificity of Examples: We evaluated the detail and specificity of the examples provided by each AI model. Points were awarded based on the concreteness and relevance of examples:
- 10 points: Numerous specific and relevant examples.
- 8-9 points: Several specific examples, but missing some details.
- 6-7 points: General examples with limited specificity.
- 5 points or below: Few or no specific examples.
Comparative Insight: This criterion looked at how well each AI compared and contrasted the ESG initiatives of the three companies. Points were awarded based on the clarity and depth of comparative insights:
- 10 points: Clear, detailed comparative analysis highlighting key differences and similarities.
- 8-9 points: Good comparative insights with minor gaps.
- 6-7 points: Basic comparative insights with significant gaps.
- 5 points or below: Limited or no comparative insights.
Identification of Conflicts: We analyzed how effectively each AI identified potential conflicts or tensions within the companies' ESG initiatives. Points were awarded based on the thoroughness of conflict identification:
- 10 points: Comprehensive identification of potential conflicts with detailed explanations.
- 8-9 points: Good identification of conflicts with minor gaps.
- 6-7 points: Basic identification of conflicts with significant gaps.
- 5 points or below: Limited or no identification of conflicts.
Overall Clarity and Structure: We rated the clarity and structure of the responses. Points were awarded based on the organization and readability of the information:
- 10 points: Exceptionally clear and well-structured response.
- 8-9 points: Clear and well-structured with minor improvements needed.
- 6-7 points: General clarity and structure with significant improvements needed.
- 5 points or below: Poorly organized and unclear response.
Each AI model was scored against this rubric, and the total scores were calculated by summing the scores across all criteria.
Google Notebook LM
Google's NotebookLM leverages Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technology combined with Large Language Models (LLMs). This approach allows the system to enhance its generative capabilities by retrieving relevant information from external sources, thus improving the accuracy and relevance of the generated content. NotebookLM, previously known as Project Tailwind, was introduced as an experimental product at Google I/O 2023. It aims to explore the potential of RAG in practical applications, particularly in processing and understanding documents stored in Google Drive. The product is powered by Google's Gemini Pro, a set of advanced multimodal models that enhance its capabilities. RAG technology is particularly useful in overcoming the limitations of LLMs, such as their reliance on pre-existing training data and the risk of generating hallucinations. By integrating high-quality retrieval systems, such as those provided by Google Search technologies, RAG ensures that the LLMs have access to fresh and relevant data, thereby improving their performance.
Claude 3.5 Sonnet
Claude 3.5 Sonnet, developed by Anthropic, is an advanced AI model known for its capabilities in complex reasoning, natural language processing, and visual interpretation. This model excels in tasks that require high levels of cognitive understanding, such as graduate-level reasoning, coding proficiency, and detailed data analysis. It operates at twice the speed of its predecessor, Claude 3 Opus, making it highly efficient for real-time applications and multi-step workflows. The model's "Artifacts" feature allows users to interact with generated content directly within the application, enhancing its utility in collaborative environments. However, it is not explicitly mentioned if Claude 3.5 Sonnet employs RAG technology, as it does not offer citations or retrieval of external data in the manner that Google Notebook LM does.
Alani AI
Alani AI utilizes Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) combined with Large Language Models (LLMs). Users can choose from seven different LLMs, including Claude 3.5 Sonnet. In this test, we used Claude 3.5 Sonnet as the foundational model along with Alani AI's proprietary RAG engine, which operates the search and retrieval of the most contextually relevant data. This combination ensures that Alani AI delivers precise, relevant, and comprehensive analysis by integrating the strengths of RAG technology with the capabilities of LLMs.
Conclusion
The evaluation of these AI models shows that Alani AI is the most proficient and useful for analyzing ESG efforts among NVIDIA, Microsoft, and Google. Its comprehensive approach, detailed examples, clear comparative insights, and well-structured responses make it the superior choice for anyone needing to perform research and make sense of large datasets. Alani AI's use of RAG technology, combined with LLMs, provides enhanced accuracy and relevance in its outputs.
This comparative analysis highlights the importance of choosing the right AI model for research, ensuring that the data is compelling and objective. With Alani AI, researchers and analysts can confidently make informed decisions backed by thorough and insightful analysis.
Ready to put your information to work?
Pick a product. Start free or talk to our team.